2022. 6. 16. 23:40ㆍ학부 강의/Android_Studio

자바 기초 기말시험 출제 포인트
- if문 swich문
- 배열(1차원, 2차원 배열)(array.length)
- for문을 while문으로, while문을 for문으로.
- 전역 변수, 지역변수, 인수, 매개변수
- try-catch문
- 클래스와 인스턴스 (필드, 메소드)
- 생성자(메소드 오버로딩)
- 상수 final, 정적 static 메소드(인스턴스 생성 없이 사용), 정적 static 필드
- 상속(메소드 오버라이딩)
- 추상클래스, 추상메소드
- 다형성
- 인터페이스, 다중상속
- 데이터 형식 변환
- 문자열 비교
- 날짜 형식
01 자바의 개요
대충 자바의 역사와 특징, 설치 방법에 대한 설명.
02 자바의 기본 문법
변수 선언 예제
public class exam02 {
public static void main(String argc[]) {
int var1 = 10;
float var2 = 10.1f;
double var3 = 10.2;
char var4 = '안';
String var5 = "안드로이드";
System.out.println(var1);
System.out.println(var2);
System.out.println(var3);
System.out.println(var4);
System.out.println(var5);
}
}자바 데이터 타입
| 표현하는 데이터 | 데이터 타입 | 데이터 크기 |
|---|---|---|
| 문자형 | char | 2byte |
| 문자형 | String | |
| 정수형 | byte | 1byte |
| 정수형 | short | 2byte |
| 정수형 | int | 4byte |
| 정수형 | long | 8byte |
| 실수형 | float | 4byte |
| 실수형 | double | 8byte |
| 참, 거짓 | boolean | ture, false |
if문
if(condition) {
// block of code to be executed if the condition is true
}if(condition) {
// block of code to be executed if the condition is ture
}else{
// block of code to be executed if the condition is false
}switch()~case
switch(number) {
case 1 :
System.out.println("case 1");
break;
case 2 :
System.out.println("case 3");
break;
case 3 :
System.out.println("case 3");
break;
default :
System.out.println("not case 1, 2, 3");
}배열
int one[] = new int[4];
one[0] = 10;
one[3] = 20;int two[][] = new int[3][4];
two[0][0] = 100;
two[2][3] = 200;int three[] = {1, 2, 3};int len = three.length;for문
for (초기식; 조건식; 증감식){
// 반복 실행할 코드
}for(변수형 변수 : 배열명) {
// 이 부분에서 변수를 사용
}while문
while(condition){
// block of code
}기말고사 : for문을 while문으로, while문을 for문으로.
전역변수(global variable), 지역변수(local variable)
public class exam05{
static int var = 100; //global
public static void main(String args[]){
int var = 0;
System.out.println(var);
int sum = addFunction(10, 20);
System.out.println(sum);
}
static int addFunction(int num1, int num2){
int hap; //local
hap = num1 + num2 + var;
return hap;
}
}try~catch
try{
System.out.println(num1/num2);
}
catch(java.lang.ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("계산에 문제가 있습니다.");
}캐스트 연산자
Button button1;
button1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn1);
//Android Studio Syntax
03 클래스와 인스턴스
클래스
클래스(class) = 변수(필드) + 메소드
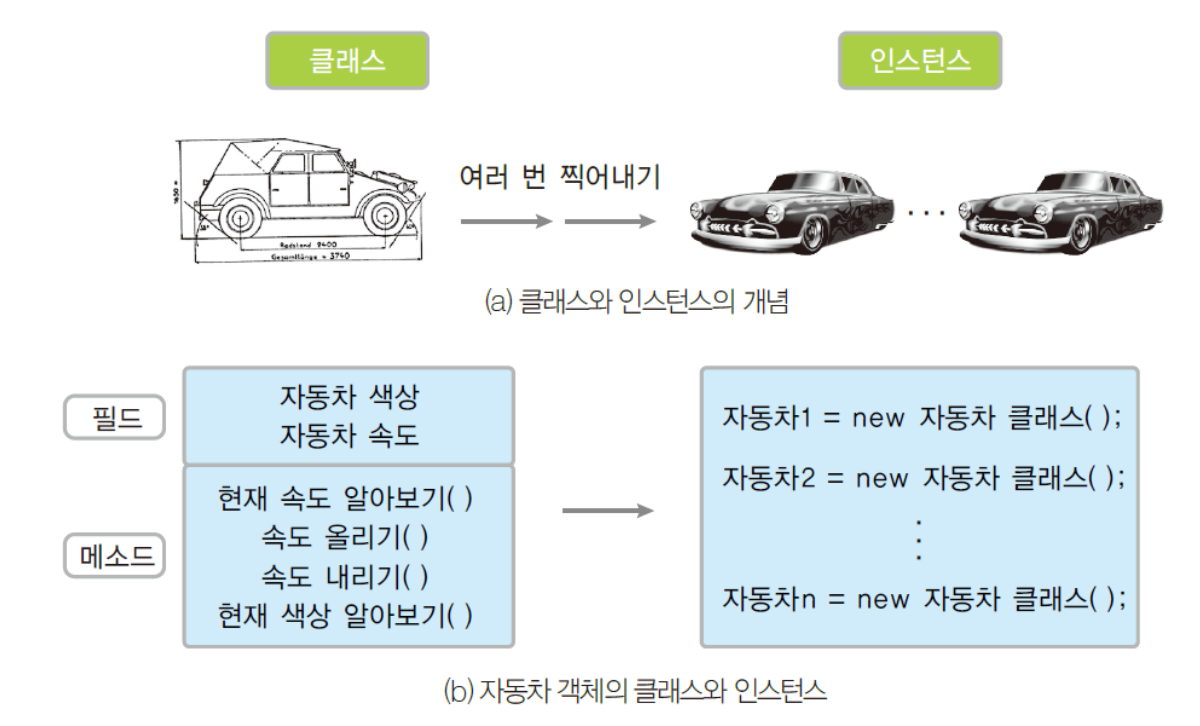
public class Car {
String color;
int speed = 0;
int getSpeed() {
return speed;
}
void upSpeed(int value) {
if (speed + value >= 200)
speed = 200;
else
speed = speed + value;
}
void downSpeed(int value) {
if (speed - value <= 0)
speed = 0;
else
speed = speed - value;
}
String getColor() {
return color;
}
}

static, final
- 정적 필드(static field) : 클래스 자체에서 사용되는 변수. 변수 앞에
static붙여 사용.
- 정적 메소드(static method) : 메소드 앞에
static붙여 사용. 인스턴스 없이 ‘클래스명.메소드명()’으로 호출해서 사용
- 상수 필드 : 정적 필드에 초기값을 입력하고
final을 앞에 붙임

04 클래스 상속
클래스 상속(inheritance)

추상 클래스와 추상 메소드
- 추상(abstract) 클래스
인스턴스화를 금지하는 클래스. 메소드 앞에 abstract 써서 사용.
- 추상 메소드
메소드 본체가 없는 메소드. 메소드 앞에 abstract 써서 사용.
추상 메소드를 포함하는 클래스는 추상 클래스로 지정해야 함.
추상 메소드를 오버라이딩하는 것을 추상 메소드를 ‘구현한다(implement)’고 함

다형성(polymorphism)
Animal 클래스인 animal에 서브 클래스인 Tiger 인스턴스를 대입한다.
animal.move 메서드를 호출해도 Tiger 클래스의 Tiger.move()가 수행된다.

인터페이스(Interface)
class 키워드 대신 interface 키워드를 사용해서 정의.
내부에는 추상 메소드를 선언.
클래스에서 인터페이스를 받아서 완성할 때 implements 키워드 사용.
Java는 다중 상속을 지원하지 않음. 대신 인터페이스를 사용하여 비슷하게 작성 가능함.


05 추가로 알아둘 자바 문법
제네릭스(Generics)
데이터 형식의 안전성을 보장하는 데 사용.
<String>뿐 아니라 <Integer>, <Double>, 사용자가 정의한 클래스형에 사용.
데이터 형식 변환
데이터형 변환을 위해 캐스팅 연산자 대신 Java에서 제공하는 클래스의 정적 메소드 사용.

문자열 비교
문자열을 비교하려면 String 클래스의 equals( ) 메소드를 사용
그냥 ==을 사용할 경우 주소가 같은지 확인한다.
그래서 내용물이 같은지 확인하기 위해선 equals()를 사용한다.

날짜 형식
날짜를 표현하기 위해 DateFormat 클래스를 사용.
이를 상속받은 SimpleDateFormat을 사용하면 ‘연월일’이나 ‘시분초’와 같은 표현이 가능.

'학부 강의 > Android_Studio' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2022-06-25 팀프로젝트_2 (보호) (0) | 2022.06.25 |
|---|---|
| 2022-06-23 팀프로젝트_1 (보호) (0) | 2022.06.23 |
| 2022-05-23 Intent_이해 (0) | 2022.05.24 |
| 2022-05-17 project_github_upload (0) | 2022.05.17 |
| 2022-05-16 Android_Studio_7 (0) | 2022.05.16 |