2023. 4. 7. 04:06ㆍCS/Compiler
Compiler
miro.com
1. Lex 파일 이해하기
가. Lex(Flex)의 입력 파일 형식
Lex(Flex)와 Yacc(Bison)의 입력 파일 모두 크게 세 부분으로 구성되어 있다.
첫 번째 부분은 선언(declaration)이나 정의(definition)를 포함한다.
두 번째 부분은 규칙(보통 번역 규칙(translation rule))을 기술한다.
세 번째 부분은 보조 프로시저(auxiliary procedure) 또는 지원 프로그램(supporting routines)를 담고 있다.
두 번째 부분은 필수고, 첫 번째, 세 번째 부분은 필요가 없는 경우 생략할 수 있다.
첫 번째, 두 번째, 세 번째는 사이에 '%%'기호로 구분한다.
예를 들어 설명해 보면…
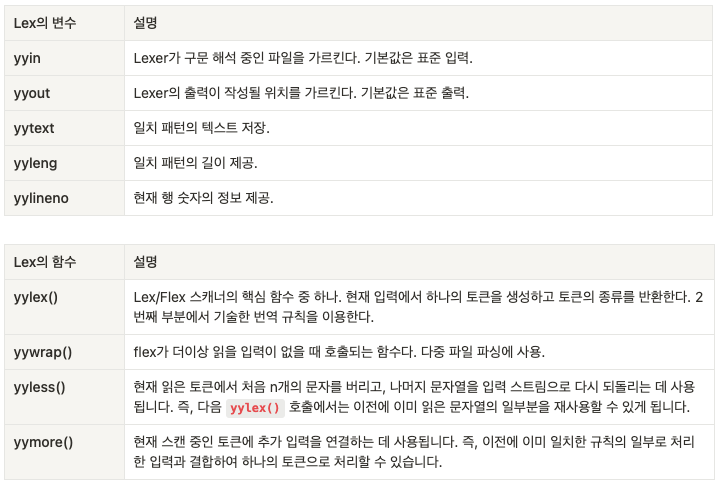
yymore()
"+" { return ADD; }
"++" { yymore(); }위의 규칙에서 첫 번째 라인은 단일 "+" 문자가 일치하면 ADD 토큰을 반환합니다.
두 번째 라인에서는 "++" 문자열이 일치하면 yymore()를 호출하고, 스캐너는 이어지는 입력을 받아들여 "+"와 결합하여 "++"을 하나의 토큰으로 처리합니다.
따라서 입력으로 "+++"이 들어오면 스캐너는 이를 "+" 토큰 두 개와 결합한 "++" 토큰과 함께 ADD 토큰을 반환합니다.
2. 정규 표현식
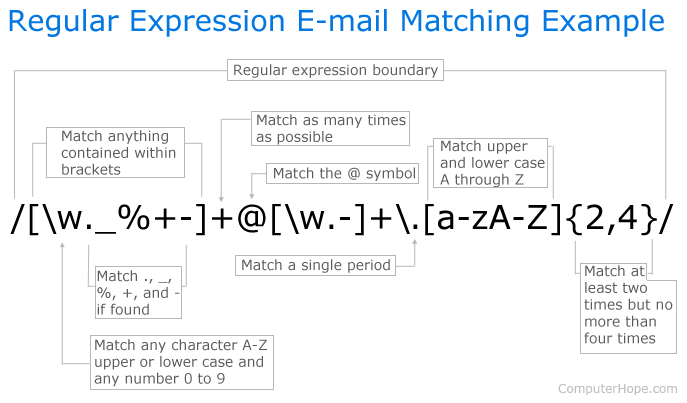
출처 : https://www.computerhope.com/jargon/r/regular-expression.gif
가. 예시
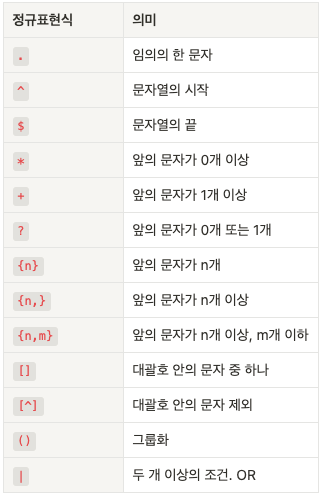
- 정규표현식
[0-9]+\\.[0-9]+?([eE][+-]?[0-9]+)?
: 소수점을 포함한 숫자와 지수 표기법으로 표현된 숫자를 포함한 문자열 표현.
다음과 같이 정규표현식을 해석할 수 있습니다.
[0-9]+: 1개 이상의 숫자\\.: 소수점[0-9]+?: 최소 1개 이상의 숫자 (+?: non-greedy matching)([eE][+-]?[0-9]+)?: 선택적으로, 지수 표기법 (e 또는 E와 함께 있는 숫자)
아래는 정규표현식에 해당하는 예시입니다.
- 123.456e+789
- 0.0001E-10
- 7.1e10
- 9.9999999999999999999999999999999999
3. scanner.l
%{
#include <stdlib.h>
/*
#define token(x) x
*/
#define EndTable(v) (v-1 + sizeof v/sizeof v[0])
int screen();
int addword(int type, char *word);
int lookup_word(char *word);
#define constant 1
#define identifier 2
#define NOTFOUND -1
%}
%%
":=" { printf("%s: ASSIGN", yytext); return(7);}
":" { printf("%s: COLON", yytext); return(8);}
"," { printf("%s: COMMA", yytext); return(9);}
"." { printf("%s: DOT", yytext); return(10);}
"=" { printf("%s: EQUAL", yytext); return(11);}
"*" { printf("%s: MULT", yytext); return(12);}
"+" { printf("%s: PLUS", yytext); return(13);}
";" { printf("%s: SEMICOL", yytext); return(14);}
[\t\n]+ { printf("%s: WhiteSpace", yytext); }
[ ]+ { printf("%s: WhiteSpace", yytext); }
[0-9][0-9]* {printf("%s: const", yytext); addword(constant, yytext); return(15);}
[a-zA-Z_][a-zA-Z0-9]* { return screen();}
%%
main(){
char *p;
while(p= (char *)yylex())
;
printf("\nsuccessful scanning.\n");
}
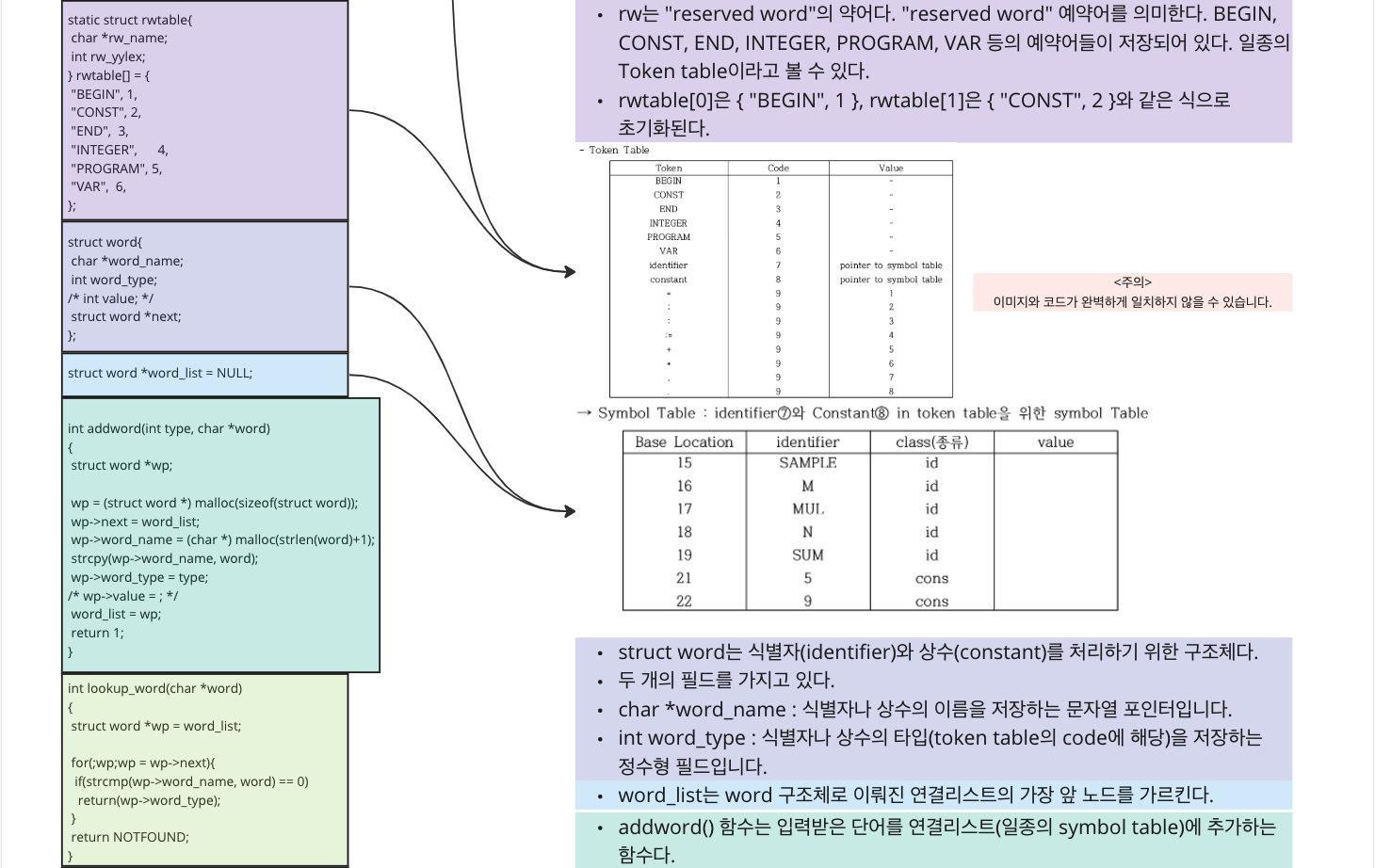
static struct rwtable{
char *rw_name;
int rw_yylex;
} rwtable[] = {
"BEGIN", 1,
"CONST", 2,
"END", 3,
"INTEGER",4,
"PROGRAM",5,
"VAR", 6,
};
struct word{
char *word_name;
int word_type;
/* int value; */
struct word *next;
};
struct word *word_list = NULL;
int addword(int type, char *word)
{
struct word *wp;
wp = (struct word *) malloc(sizeof(struct word));
wp->next = word_list;
wp->word_name = (char *) malloc(strlen(word)+1);
strcpy(wp->word_name, word);
wp->word_type = type;
/* wp->value = ; */
word_list = wp;
return 1;
}
int lookup_word(char *word)
{
struct word *wp = word_list;
for(;wp;wp = wp->next){
if(strcmp(wp->word_name, word) == 0)
return(wp->word_type);
}
return NOTFOUND;
}
int screen()
{
struct rwtable *low = rwtable,
*high = EndTable(rwtable),
*mid;
int c;
while(low <= high){
mid = low + (high - low)/2;
if((c = strcmp(mid->rw_name, yytext)) == 0){
printf("%s: keyword", yytext);
return(mid->rw_yylex);
}
else{
if(c < 0)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
}
if(lookup_word(yytext) != NOTFOUND){
printf("%s: id", yytext);
return(16);
}
else{
addword(identifier, yytext);
printf("%s: id", yytext);
return(16);
}
}


출처 : http://pds27.egloos.com/pds/201305/07/70/lex-yacc-tutorial.pdf
출처 : https://www.ibm.com/docs/ko/aix/7.2?topic=l-lex-command
출처 : https://zyint.tistory.com/65
출처 : https://infinitt.tistory.com/318
'CS > Compiler' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Compiler] 유도 트리 (0) | 2023.04.15 |
|---|---|
| [Compiler] 구문 분석 (0) | 2023.04.15 |
| [Compiler] Flex 실습 (0) | 2023.03.31 |
| [Compiler] Scanner 구현 과정 (0) | 2023.03.31 |
| [Compiler] 유한 상태 기계 (0) | 2023.03.31 |