2024. 1. 28. 21:32ㆍ공부 중/Java
1. Collection Framework
데이터를 저장하기 위한 개발자들의 몸부림.
- 배열 : 동일한 데이터 타입만 관리 가능
- Object 배열 : 런타임에 실제 객체의 타입 확인 후 사용해야 함.
- Generic : 형변환의 번거로움 제거
한계점 : 한번 정해진 배열의 크기를 변경할 수 없다.
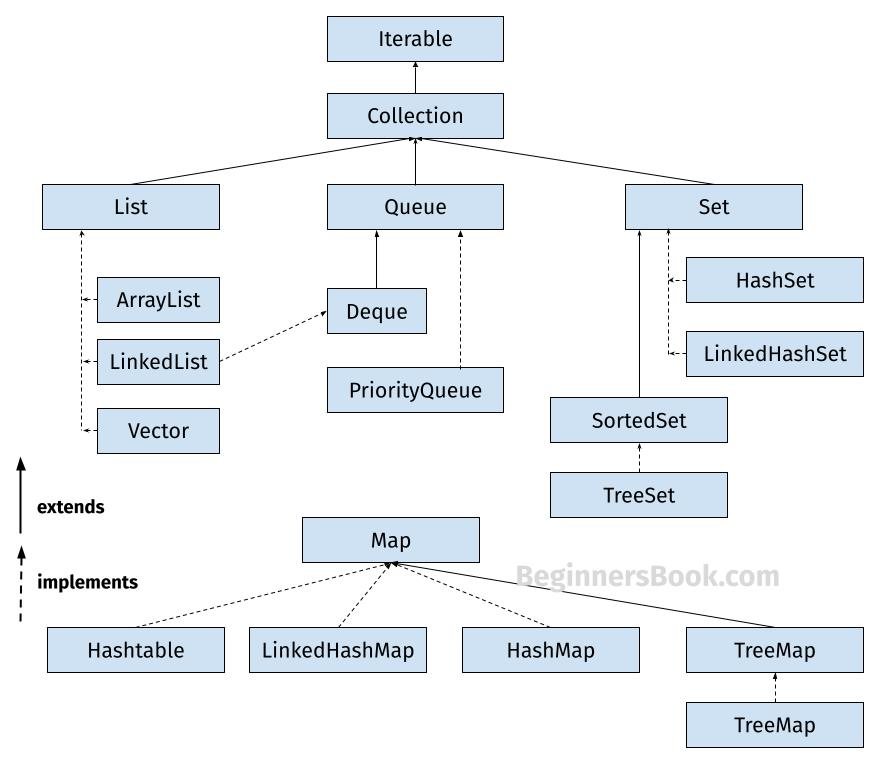
이미지 출처 : https://beginnersbook.com/java-collections-tutorials/
모든 Collection은 Iterator interface를 구현한다.
Iterator는 3 가지 메서드를 가지고 있다.

이러한 기능을 조합하면 다수의 데이터를 순차적으로 처리할 수 있다.
Iterator (Java Platform SE 7 )
An iterator over a collection. Iterator takes the place of Enumeration in the Java Collections Framework. Iterators differ from enumerations in two ways: Iterators allow the caller to remove elements from the underlying collection during the iteration with
docs.oracle.com
- 3대 주요 인터페이스.
| interface | 특징 | 중복 | 종류 |
| List | 입력 순서가 있는 데이터의 집합. | 가능 | ArrayList, LinkedList |
| Set | 입력 순서를 유지하지 않는 데이터의 집합. | 불가능 | HashSet, TreeSet |
| Map | Key와 value의 쌍으로 데이터를 관리하는 집합. | Key 중복 불가, value 중복 가능 | HashMap, TreeMap |
- Collection interface
| 분류 | 메서드 |
| 추가 | add(E e), addAll(Collection<? extends E> c |
| 조회 | contains(Object o), cotainsAll(Collection<?> c), equals(), isEmpty(), iterator(), size() |
| 삭제 | clear(), remove(Object o), removeAll(Collection<?> c) |
| 수정 | |
| 기타 | toArray() |
2. List 계열
입력 순서가 있는 데이터의 집합.
입력 순서가 있으므로 데이터의 중복이 가능.
구현체로는 Vector, Stack, ArrayList, LinkedList가 있다.
가. 주요 메서드
분류 Collection List
| 분류 | Collection | List |
| 추가 | add(E e), addAll(Collection<? extends E> c | add(int index, E element), addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) |
| 조회 | contains(Object o), cotainsAll(Collection<?> c), equals(), isEmpty(), iterator(), size() |
get(int index), indexOf(Object o), lastIndexOf(Object o), listIterartor() |
| 삭제 | clear(), remove(Object o), removeAll(Collection<?> c), retainAll(Collection<?> c) |
remove(int index) |
| 수정 | set(int index, E element) | |
| 기타 | toArray() | subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex), sort(Comparator<? super E> c) |
List (Java Platform SE 8 )
An ordered collection (also known as a sequence). The user of this interface has precise control over where in the list each element is inserted. The user can access elements by their integer index (position in the list), and search for elements in the lis
docs.oracle.com
나. 예제
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListTest {
List<String> friends = new ArrayList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
ListTest alt = new ListTest();
alt.createTest();
alt.retrieveTest();
alt.updateTest();
alt.deleteTest();
}
public void createTest() {
friends.add("홍길동");
friends.add("임꺽정");
friends.add(1, "장길산");
friends.add("홍길동"); // 데이터 중복 가능
System.out.println("추가 후 내용 출력: " + friends);
}
public void retrieveTest() {
System.out.println(friends.isEmpty() + " : "+ friends.size());
for(String name : friends) {
System.out.println(name);
}
System.out.println(friends.indexOf("홍길동") + " : " + friends.lastIndexOf("홍길동"));
}
public void updateTest() {
int idx = friends.indexOf("홍길동");
if(idx >= 0) {
friends.set(idx, "율도국 왕");
}
System.out.println("수정 후 : "+friends);
}
public void deleteTest() {
friends.remove(0);
friends.remove("율도국 왕");
System.out.println("삭제 후 : " + friends);
friends.clear();
System.out.println("초기화 후 : " + friends);
}
}
/*
추가 후 내용 출력: [홍길동, 장길산, 임꺽정, 홍길동]
false : 4
홍길동
장길산
임꺽정
홍길동
0 : 3
수정 후 : [율도국 왕, 장길산, 임꺽정, 홍길동]
삭제 후 : [장길산, 임꺽정, 홍길동]
초기화 후 : []
*/List<String> friends = new ArrayList<>();
:List는 인터페이스.ArrayList가 구현체.
:Array<String> friends로 컴파일러가 수정해서 컴파일 진행함. (최적화)- 뒤에
<>비어있는 이유는List<String>에 있어서 생략한 것. 두 줄로 나눠 쓰면 채워줘야 함. createTest():add(E e),add(int index, E element)를 활용한 추가.retrieveTest(): List의 요소를 순회하는 법.updateTest():indexOf(Object o),set(int index, E element)를 활용한 수정deleteTest():remove(Object o),remove(int index)를 활용한 삭제
다. ArrayList
constructor를 살펴보면 내부적으로 Object[] 사용.
하지만 Collection에는 정해진 크기가 없다.
//add → ensureCapacityInternal → ensuerExplicitCapacity → grow
...
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);이는 크기가 부족하면 알아서 크기를 늘려주기 때문이다.(2배씩 증가)
처음 크기는 기본적으로 10이다.
크기는 필요에 의해서 객체를 생성할 때 전달할 수 있다. (new ArrayList<>(int initialCapacity))
만약 필요한 크기를 대략적으로 알고 있다면 미리 지정하는 것이 좋다.
배열을 사용하는 ArrayList도 배열의 장-단점을 일부 가지고 있다.
- 장점
- 빠르고 사용하기 쉽다.
- 단점
- 크기를 변경할 수 없어서 크기를 키우려면 새로운 배열을 만들고 복사해야 한다.
- 비순차적 데이터의 추가, 삭제에 많은 시간이 걸린다.
마. LinkedList
각 요소를 Node로 정의한다.
각 Node는 데이터와 다음 Node의 참조 값을 가지고 있다.
Node의 참조값만 수정하면 손쉽게 Node를 추가 및 삭제할 수 있다.
바. LinkedList vs ArrayList
용도에 적합한 특정 클래스를 사용해야 한다.
정적인 데이터 활용, 단순한 데이터 조회용 → ArrayList
동적인 데이터 추가, 삭제가 많은 작업 → LinkedList
다행히 둘 다 List 인터페이스의 구현체이기 때문에 변경이 쉽다.
List<String> friends = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> friends = new LinkedList<>();
사. 자료 삭제 시 주의점
1) index를 이용한 for문
for(int i=0; i<nums.size(); i++){
if(nums.get(i)%2==1){
nums.remove(i);
i--;
}
}지우면서 요소들도 이동하기 때문에 지우는 경우 i--가 반드시 필요하다.
for(int i=nums.size()-1; i>=0; i--){
if(nums.get(i)%2==1) {
nums.remove(i);
}
}뒤에서부터 거꾸로 접근하면 해결할 수 있다.
2) 향상된 for문
for(Integer num : nums) {
if(num%2==1){
nums.remove(num); // Exception!
}
}향상된 for문 (또는 for-each)문은 Collection 크기가 변하면 안 된다.
3. Set 계열
입력 순서를 관리하지 않는다.
중복을 허용하지 않아서 중복을 제거하는 효율적인 방법이다.
구현체로는 HashSet과 TreeSet이 있다.
TreeSet은 이진트리로 정렬되어 있다.
가. 예제
public class SetTest {
Set<Object> hset = new HashSet<Object>();
private void addMethod(){
hset.add(new Integer(1));
hset.add(1);
hset.add("중복");
hset.add("중복");
System.out.println("데이터 추가: "+ hset);
}
private void retrieveMethod(){
System.out.println("데이터 개수: " + hset.size());
for(Object obj : hset){
System.out.println("데이터 조회: " + obj);
}
}
private void removeMethod() {
hset.remove("중복");
System.out.println("데이터 삭제 결과: " + hset);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
SetTest test = new SetTest();
test.addMethod();
test.retrieveMethod();
test.removeMethod();
}
}
/*
데이터 추가: [1, 중복]
데이터 개수: 2
데이터 조회: 1
데이터 조회: 중복
데이터 삭제 결과: [1]
*/hset.add(new Integer(1));,hset.add("중복");: 데이터 추가hset.size(): Set의 크기hset.remove("중복");: 데이터 제거
index로 관리하지 않기 때문에 update는 할 수 없다.
나. 주요 메서드
| 분류 | Collection | Set |
| 추가 | add(E e), addAll(Collection<? extends E> c | |
| 조회 | contains(Object o), cotainsAll(Collection<?> c), equals(), isEmpty(), iterator(), size() |
|
| 삭제 | clear(), remove(Object o), removeAll(Collection<?> c), retainAll(Collection c) | |
| 수정 | ||
| 기타 | toArray() |
Set (Java Platform SE 8 )
A collection that contains no duplicate elements. More formally, sets contain no pair of elements e1 and e2 such that e1.equals(e2), and at most one null element. As implied by its name, this interface models the mathematical set abstraction. The Set inter
docs.oracle.com
다. 동일한 데이터의 기준
- 객체의
equals()가true이며 hashCode()값이 같은 경우 (실제로 참조하는 객체가 같은가?)
그래서 Hash를 이용하는 Collection을 사용하는 경우 반드시 hashCode()를 재정의해야 한다.
4. Map 계열
Key와 Value를 하나의 Entry로 묶어서 데이터 관리.
- key : Object, 중복 불가.
- value : Object, 중복 가능.
대표적인 구현체로는 HashMap, TreeMap(정렬됨)가 있다.
나. 주요 메서드
| 분류 | Collection | Map |
| 추가 | add(E e), addAll(Collection<? extends E> c | put(K key, V value), putAll(Map<? extends K, ?extends V>m), putIfAbsent(K Key, V value) |
| 조회 | contains(Object o), cotainsAll(Collection<?> c), equals(), isEmpty(), iterator(), size() |
containsKey(Object key), containsValue(Object value), entrySet(), keySet(), get(Obejct key), values() |
| 삭제 | clear(), remove(Object o), removeAll(Collection<?> c) |
remove(Object key) |
| 수정 | put(K key, V value), putAll(Map<? extends K, ?extends V>m), putIfAbsent(K Key, V value) |
|
| 기타 | toArray() |
Map의 key와 entry는 Set으로 관리된다. (entrySet(), keySet() → Set 반환)
Map의 key는 유일하기 때문에 추가와 수정에 사용되는 메서드는 동일하다.
이외에도 다양한 메서드가 존재한다.
Map (Java Platform SE 8 )
If the specified key is not already associated with a value (or is mapped to null), attempts to compute its value using the given mapping function and enters it into this map unless null. If the function returns null no mapping is recorded. If the function
docs.oracle.com
다. 예제
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapTest {
Map<String, String> hMap = new HashMap<>();
private void addMethod() {
// 동일한 키의 사용은 불가.
hMap.put("andy", "1234");
hMap.put("andy", "4567"); // 수정, 덮어쓰기
hMap.put("kate", "9999");
hMap.putIfAbsent("kate", "1234"); // 기존에 해당 키에 대한 값이 없을 때만 추가
// 동일한 값은 추가됨.
hMap.put("henry", "4567");
hMap.put("hong", "1234");
System.out.println("추가 결과: " + hMap);
// 추가 결과: {hong=1234, henry=4567, kate=9999, andy=4567}
}
private void retrieveMethod() {
// map이 가지고 있는 key와 거기에 연결된 value를 출력.
System.out.println(hMap.get("kate")); // 9999
System.out.println(hMap.containsKey("kate")); // true
Set<String> keys = hMap.keySet();
for(String key: keys) {
System.out.println("key: " + key + ", value: " + hMap.get(key));
}
/*
key: hong, value: 1234
key: henry, value: 4567
key: kate, value: 9999
key: andy, value: 4567
*/
Set<Entry<String, String>> entries = hMap.entrySet();
for(Entry<String, String> entry: entries) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : "+entry.getValue());
}
/*
hong : 1234
henry : 4567
kate : 9999
andy : 4567
*/
// value로 key를 찾을때
Set<Entry<String, String>> entries2 = hMap.entrySet();
for(Entry<String, String> entry: entries2) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " : " + entry.getValue());
if(entry.getValue().equals("4567")) {
System.out.println("발견");
}
}
/*
hong : 1234
henry : 4567
발견
kate : 9999
andy : 4567
발견
*/
}
private void removeMethod() {
hMap.remove("andy");
hMap.clear();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MapTest hmt = new MapTest();
hmt.addMethod();
hmt.retrieveMethod();
hmt.removeMethod();
}
}
/*
추가 결과: {hong=1234, henry=4567, kate=9999, andy=4567}
9999
true
key: hong, value: 1234
key: henry, value: 4567
key: kate, value: 9999
key: andy, value: 4567
hong : 1234
henry : 4567
kate : 9999
andy : 4567
hong : 1234
henry : 4567
발견
kate : 9999
andy : 4567
발견
*/hMap.put("andy", "4567");: 추가와 수정이 같다. 기존의 값을 덮어쓴다.hMap.putIfAbsent("kate", "1234");: 기존에 해당 키에 대한 값이 없을 때만 추가하는 법.Set<String> keys = hMap.keySet();: key로 map을 순회할 때.Set<Entry<String, String>> entries2 = hMap.entrySet();: value로 map을 순회할 때.
5. 정렬
순서를 가지는 Collection들만 정렬 가능.
List계열SortedSet의 자식 객체SortedMap의 자식 객체 (key 기준)
객체가 Comparable을 상속 및 구현하고 있는 경우 java.util.Collections.sort() 이용해 정렬할 수 있음.
Collections (Java Platform SE 8 )
Rotates the elements in the specified list by the specified distance. After calling this method, the element at index i will be the element previously at index (i - distance) mod list.size(), for all values of i between 0 and list.size()-1, inclusive. (Thi
docs.oracle.com
(Collection에 대한 sort(), max(), min(), fill(), frequency(), reverse() 등 유용한 기능을 지원하는 클래스)
private List<String> names = Arrays.asList("Hi", "Java", "World", "Welcome", ");
public void basicSort() {
Collections.sort(names);
System.out.println(names);
}
//[!, Hi, Java, Welcome, World]Comparable을 상속 및 구현하고 있지 않으면 Comparable을 직접 상속받아서 구현해야 한다.
가. Comparable interface
public interface Comparable<T> {
public int compareTo(T p);
}- 반환값이…
- 양수 : 자리 바꿈
- 음수 : 자리 유지
- 0 : 동일 위치
// SmartPhone을 다른 SmartPhone과 번호를 기준으로 비교
public class SmartPhone implements Comparable<SmartPhone> {
String number;
public SmartPhone(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
public String toString() {
return "전화 번호: " + number;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(SmartPhone o) {
return this.number.compareTo(o.number);
}
}implements Comparable<SmartPhone>: 인터페이스 구현.public int compareTo(SmartPhone o) {…}: 재정의.return this.number.compareTo(o.number);: 이미 정의된String.compare()활용.
import java.util.Collections;
...
public void stringLengthSort() {
List<SmartPhone> phones = Arrays.asList(new SmartPhone("010"), new SmartPhone("011"), new SmartPhone("000"));
Collections.sort(phones);
System.out.println(phones);
}
/*
[전화 번호: 000, 전화 번호: 010, 전화 번호: 011]
*/
나. Comparator
우리가 소스코드를 수정할 수 없는 경우 Comparable을 구현할 수 없다.
또는 사용자 정의 알고리즘으로 정렬하려는 경우.
import java.util.Comparator;
public class StringLengthComparator implements Comparator<String>{
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
int len1 = o1.length();
int len2 = o2.length();
return Integer.compare(len1, len2);
}
}return Integer.compare(len1, len2);:Integer.compare()를 활용.
문자열을 길이를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬하고 있다.
private List<String> names2 = Arrays.asList("Hi", "Java", "World", "Welcome", "!");
public void stringLengthSort() {
Collections.sort(names2, new StringLengthComparator());
System.out.println(names2);
}
// [!, Hi, Java, World, Welcome]
'공부 중 > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java] File IO (0) | 2024.01.29 |
|---|---|
| [Java] 람다식 (0) | 2024.01.28 |
| [Java] 예외 처리 (0) | 2024.01.28 |
| [Java] String (0) | 2024.01.22 |
| [Java] 인터페이스 (0) | 2024.01.22 |