2024. 2. 25. 22:03ㆍAlgorithm/with Java
1. 그래프
- 정점 간의 관계를 간선으로 표현한 것.
간선의 방향에 따라서 무향 그래프(양방향 그래프), 유향 그래프로 나뉠 수 있다.
밀집도에 따라서 완전 그래프, 밀집 그래프 그리고 희소 그래프로 나뉜다.
이 외에도 가중치 그래프, 사이클 없는 그래프 등 다양한 그래프가 존재한다.
그래프를 표현하는 방식은 크게 3가지 있다.
| 그래프 표현 방식 | 설명 | 시간 복잡도 (연결 여부 확인) |
공간 복잡도 | 특징 |
| 인접 행렬 | 그래프의 노드들을 2차원 배열에 저장. 배열의 행과 열은 각각 그래프의 노드를 의미하며, 배열의 값은 두 노드 간의 간선 유무(또는 가중치)를 의미함. | O(1) | O(V^2) | -구현이 쉽다. -진입 차수를 구하기 쉽다. -밀집 그래프에 유리한다. |
| 인접 리스트 | 각 노드에 연결된 노드들을 리스트로 저장. 각 노드를 표현하는 객체 또는 배열의 각 인덱스는 리스트의 시작점을 참조함. | O(V) | O(E+V) | -공간복잡도가 낮다. -연결 여부를 확인하는 시간 복잡도가 높다. |
| 간선 리스트 | 그래프의 모든 간선을 하나의 리스트로 저장. 각 간선은 연결된 두 노드를 표현하는 정보를 가지고 있음. | O(E) | O(E) | -공간복잡도가 낮다. -연결 여부를 확인하는 시간 복잡도가 높다. |
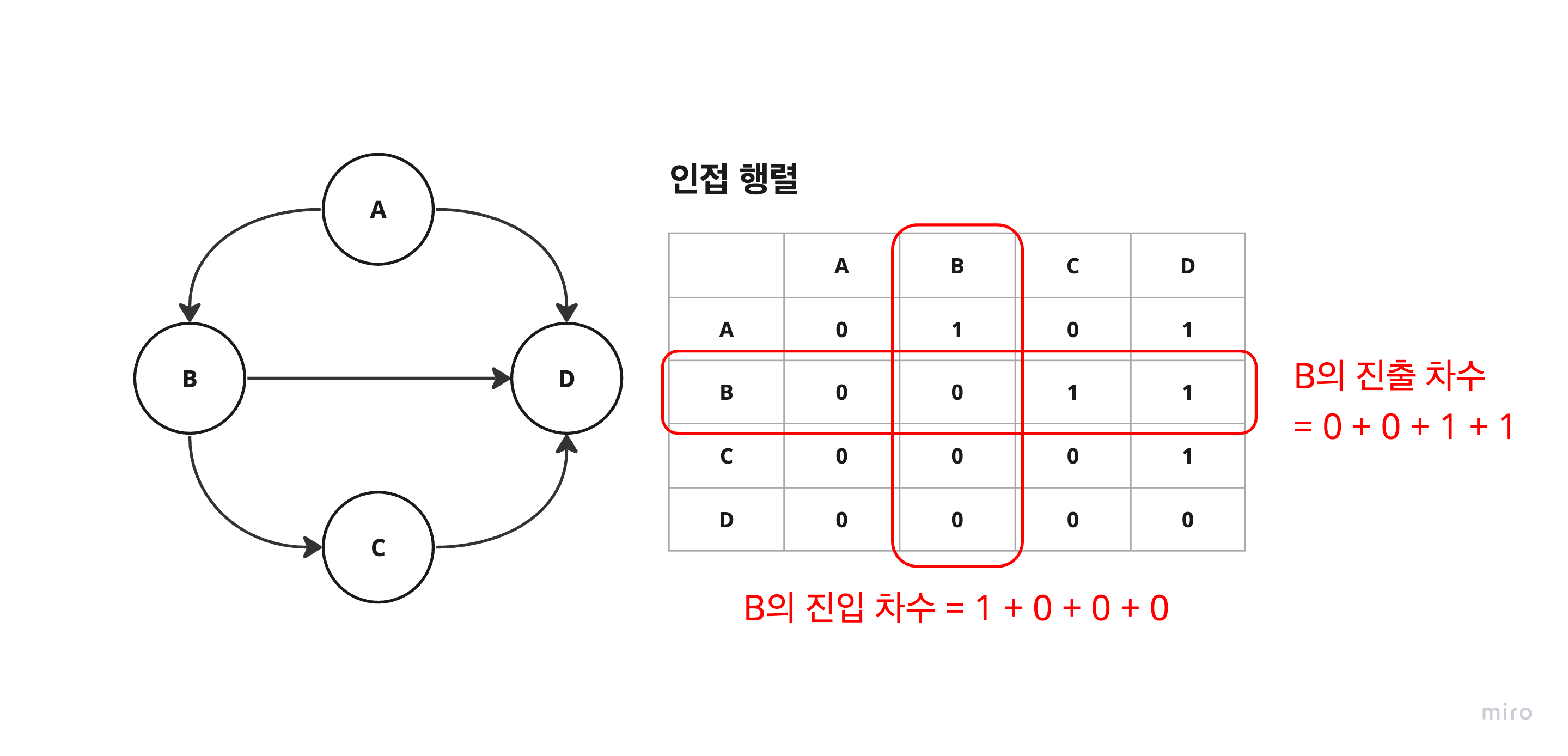
2. 인접 행렬
- 노드를 2차원 배열에 저장. 배열의 행과 열은 각각 그래프의 노드를 의미한다.
- 배열의 값은 두 노드 간의 간선 유무 또는 가중치를 의미함.
- 시간 복잡도(연결 여부 확인) :
O(1) - 공간 복잡도 :
O(V^2)
- 장점
- 밀집 그래프에 유리. (대략 40% 이상).
- 진입 차수를 구하기 쉽다. 역추적에 유리.
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjMatrixTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
int[][] adjMatrix = new int[V][V];
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) { // 간선 저장
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
adjMatrix[to][from] = adjMatrix[from][to] = 1; // 양방향
}
for(int[] row : adjMatrix) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(row));
}
sc.close();
}
}
/*
7
8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
4 3
5 3
5 4
6 4
*/
- 응용
- 최소신장트리 : 프림
- 최단경로 : 다익스트라
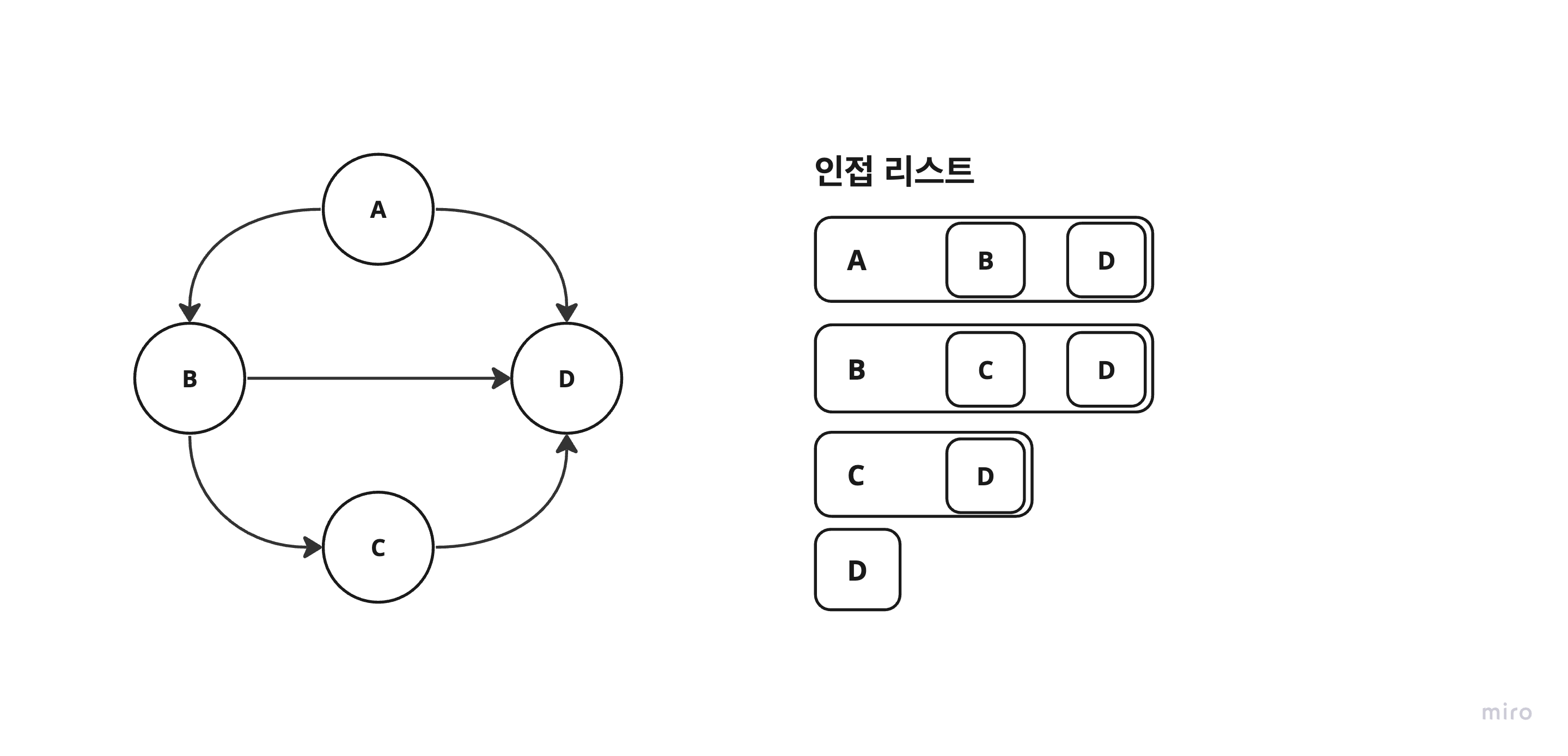
3. 인접 리스트
- 각 정점에 대한 인접 정점들을 순차적으로 표현.
- 하나의 정점에 대한 인접 정점들을 각각 노드로 하는 연결 리스트로 저장.
- 시간 복잡도(연결 여부 확인) :
O(V) - 공간 복잡도 :
O(V+E)
- 장점
- 희소 그래프에 유리. (대략 40% 이하)
- 공간복잡도가 낮음.
// Node
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjListTest {
private static class Node{
int to;
Node next;
public Node(int to, Node next) {
this.to = to;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(int to) {
this.to = to;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return to + " " + next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
Node node;
Node[] adjList = new Node[V];
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) { // 간선 저장
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
// from -> to
node = new Node(to, adjList[from]);
adjList[from] = node;
// to -> form
node = new Node(from, adjList[to]);
adjList[to] = node;
}
for(int i=0; i<V; i++) {
System.out.println("from=" + i + " to= " + adjList[i]);
}
sc.close();
}
}
/*
7
8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
4 3
5 3
5 4
6 4
*/Node 클래스를 정의해서 인접리스트를 구현하는 방법이다.
// ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjListTest3 {
private static class Data {
int to;
int weight;
Data(int to, int weight){
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Data [to=" + to + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
List<Data>[] list = new ArrayList[V+1]; // index가 1부터 시작
for(int i=0; i<=V; i++) {
list[i] = new ArrayList<Data>();
}
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) {
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
int weight = sc.nextInt();
list[from].add(new Data(to, weight));
list[to].add(new Data(from, weight));
}
for(List<Data> l : list) {
System.out.println(l);
}
sc.close();
}
}
/*
7
8
1 2 10
1 3 23
1 6 43
1 7 33
5 4 65
6 4 12
6 5 11
7 5 55
*/ArrayList를 사용해서 인접리스트를 구현하는 방법이다.
- 응용
- 최소신장트리 : 프림
- 최단경로 : 다익스트라
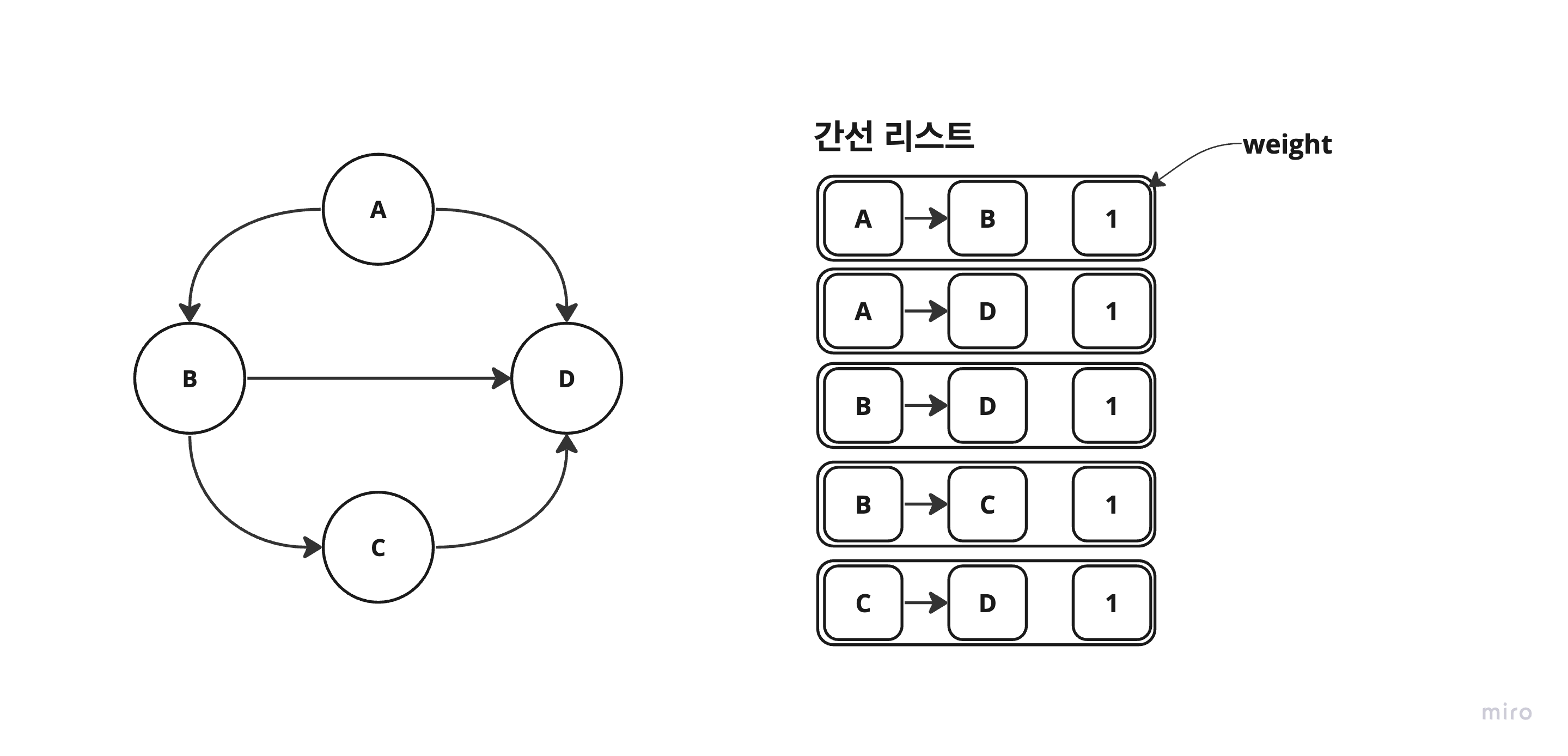
4. 간선 리스트
- 간선(시작 정점, 끝 정점)의 정보를 객체로 표현하여 리스트에 저장.
- 시간 복잡도(연결 여부 확인) :
O(E) - 공간 복잡도 :
O(E)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class EdgeListGraph {
private static class Edge {
int start;
int end;
public Edge(int start, int end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
List<Edge> edgeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int start = sc.nextInt();
int end = sc.nextInt();
Edge edge = new Edge(start, end);
edgeList.add(edge);
}
for (Edge edge : edgeList) {
System.out.println("Start: " + edge.start + " End: " + edge.end);
}
sc.close();
}
}
- 응용
- 최소신장트리 : 크루스칼
- 최단경로 : 벨만포드
5. BFS
- 최단 거리를 구하는 것에 유리하다.
가. 인접 행렬
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjMatrixTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
int[][] adjMatrix = new int[V][V];
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) { // 간선 저장
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
adjMatrix[to][from] = adjMatrix[from][to] = 1; // 양방향
}
bfs(adjMatrix, 0);
sc.close();
}
static void bfs(int[][] adjMatrix, int start) {
int V = adjMatrix.length;
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
boolean[] vis = new boolean[V];
// 시작점을 큐에 넣고 방문체크
queue.offer(start);
vis[start] = true;
// 큐로 방문체크
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cur = queue.poll();
System.out.println((char)(cur+65));
for(int i=0; i<V; i++) {
// 인접 정점 체크
if(adjMatrix[cur][i] == 0 || vis[i]) continue;
queue.offer(i);
vis[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
/*
7
8
0 1
0 2
1 3
1 4
2 4
3 5
4 5
5 6
*/
나. 인접 리스트
// Node
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdjListTest {
private static class Node{
int to;
Node next;
public Node(int to, Node next) {
this.to = to;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(int to) {
this.to = to;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return to + " " + next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int V = sc.nextInt();
int E = sc.nextInt();
Node node;
Node[] adjList = new Node[V];
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) { // 간선 저장
int from = sc.nextInt();
int to = sc.nextInt();
// from -> to
node = new Node(to, adjList[from]);
adjList[from] = node;
// to -> form
node = new Node(from, adjList[to]);
adjList[to] = node;
}
bfs(adjList, 0);
sc.close();
}
static void bfs(Node[] adjList, int start) {
int V = adjList.length;
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
boolean[] vis = new boolean[V];
// 시작점을 큐에 넣고 방문체크
queue.offer(start);
vis[start] = true;
// 큐로 방문체크
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int cur = queue.poll();
System.out.println((char)(cur+65));
for(Node tmp = adjList[cur]; tmp != null; tmp=tmp.next) {
// 인접 정점 체크
if(vis[tmp.to]) continue;
queue.offer(tmp.to);
vis[tmp.to] = true;
}
}
}
}
/*
7
8
0 1
0 2
1 3
1 4
2 4
3 5
4 5
5 6
*/
6. DFS
- 최대 거리를 찾을 때 유리하다.
가. 인접 행렬
static void dfs(int[][] adjMatrix, boolean[] visited, int current) {
int V= adjMatrix.length;
visited[current] = true;
System.out.println((char)(current+65));
for(int i=0; i<V; i++) {
if(adjMatrix[current][i] != 0 && !visited[i]) {
dfs(adjMatrix, visited, i);
}
}
}
나. 인접 리스트
static void dfs(Node[] adjList, boolean[] visited, int current) {
visited[current] = true;
System.out.println((char)(current+65));
for(Node tmp = adjList[current]; tmp != null; tmp = tmp.next) {
if(!visited[tmp.to]) {
dfs(adjList, visited, tmp.to);
}
}
}13023번: ABCDE
문제의 조건에 맞는 A, B, C, D, E가 존재하면 1을 없으면 0을 출력한다.
www.acmicpc.net
7. Flood Fill 알고리즘
- 그래프가 주어질 때, 특정한 시작점으로부터 연결된 영역을 찾는 알고리즘.
- 4방향 탐색, 8방향 탐색 (대각선)
- 구현
- BFS 알고리즘을 이용하여
Queue로 구한하거나, - DFS 알고리즘을 이용하여 재귀 함수로 구현.
- BFS 알고리즘을 이용하여
8. 위상 정렬
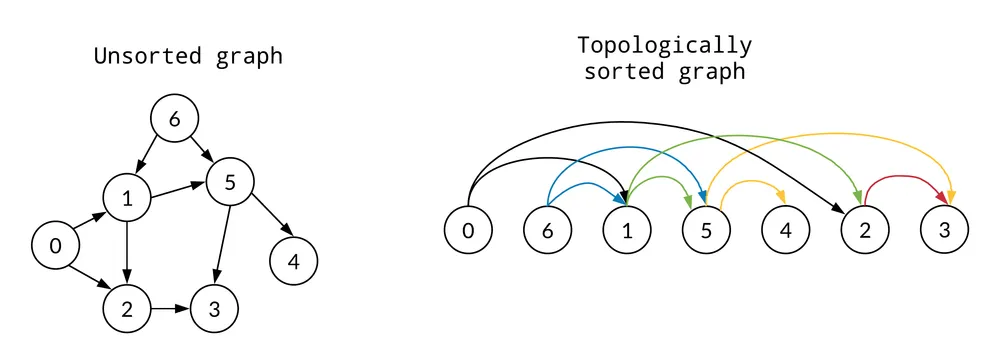
- topological sorting
- 순환하지 않는 유향 그래프를 방향성에 거스르지 않도록 순서대로 배열하는 방법.
- 순서가 정해져 있는 작업들을 차례대로 수행해야 할 때, 그 순서를 결정해 주는 알고리즘.
- BFS, DFS로 구현할 수 있다. (BFS를 많이 사용한다.)
가. BFS
- 진입 차수가 0인 노드를 큐에 넣는다. (그룹 내에서 가장 앞선 노드)
- 큐에서 노드를 꺼낸다. 꺼낸 노드와 인접한 모든 노드들에 대하여 간선을 제거한다. (= 인접한 노드의 진입 차수를 1 감소시킨다.)
- 간선 제거 후 진입 차수가 0이 된 노드를 큐에 넣는다.
- 큐가 빌 때까지 2, 3번 작업을 반복한다.
public class BOJ2252 {
static int N, M; // 정점의 수, 간선의 수
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 정점
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 간선
// 진입 차수 관리
int[] inDegree = new int[N+1];
// 연결 리스트 초기화
ArrayList<Integer>[] list = new ArrayList[N+1]; // 1 ~ N
int size = N+1;
for(int i=0; i<size; i++) {
list[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
int from, to;
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
from = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
to = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
list[from].add(to);
inDegree[to]++; // 진입 차수 개수를 센다.
}
// 구현 (위상 정렬)(BFS로 구현)
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 1. 진입 차수가 0인 노드를 큐에 넣는다.
for(int i=1; i<size; i++) { // 1 ~ N
if(inDegree[i]==0) q.offer(i);
}
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
// 2. 꺼낸 노드와 인접한 모든 노드들에 대하여 간선을 제거한다. (= 진입 차수를 1 감소)
int cur = q.poll();
res.add(cur);
for(int idx : list[cur]) {
inDegree[idx]--;
// 3. 간선 제거 후 진입 차수가 0이 된 노드를 큐에 넣는다.
if(inDegree[idx] == 0)
q.offer(idx);
}
}
// res.size() == N이면 위상 정렬 성공
// res.size() != N이면 위상 정렬 실패
//if(ret.size()!=N){ // 위상 정렬이 불가능 -> 순환 발생
// System.out.println(0);
// return;
//}
// 출력
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for(Integer i : res) {
sb.append(i).append(" ");
}
System.out.println(sb);
br.close();
}
}int[] inDegree = new int[N+1];: 진입 차수를 따로 관리한다.
만약 while문이 종료된 후 res.size() == N이면 위상 정렬 성공한 것이고 res.size() != N이면 위상 정렬 실패한 것이다.
실패한 경우 순환하는 그래프라는 의미다.
보통 정렬이 가능한 경우의 수 중에서 아무거나 하나를 구하거나 정렬이 가능한지 아닌지 구하는 문제가 나온다.
2252번: 줄 세우기
첫째 줄에 N(1 ≤ N ≤ 32,000), M(1 ≤ M ≤ 100,000)이 주어진다. M은 키를 비교한 회수이다. 다음 M개의 줄에는 키를 비교한 두 학생의 번호 A, B가 주어진다. 이는 학생 A가 학생 B의 앞에 서야 한다는 의
www.acmicpc.net
2623번: 음악프로그램
첫째 줄에는 가수의 수 N과 보조 PD의 수 M이 주어진다. 가수는 번호 1, 2,…,N 으로 표시한다. 둘째 줄부터 각 보조 PD가 정한 순서들이 한 줄에 하나씩 나온다. 각 줄의 맨 앞에는 보조 PD가 담당한
www.acmicpc.net
'Algorithm > with Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 1260. DFS와 BFS (0) | 2024.02.25 |
|---|---|
| [알고리즘] 2252. 줄 세우기 (0) | 2024.02.25 |
| [알고리즘] 풀었던 문제 (240213 ~ 16) (0) | 2024.02.19 |
| [알고리즘] 7576. 토마토 (0) | 2024.02.19 |
| [알고리즘] 1247. 최적경로 (0) | 2024.02.19 |