2023. 3. 1. 21:14ㆍ공부 중/Node.js
0. 참고자료
Setup and Teardown · Jest
Often while writing tests you have some setup work that needs to happen before tests run, and you have some finishing work that needs to happen after tests run. Jest provides helper functions to handle this.
jestjs.io
1. 설정 및 해제
테스트를 작성하는 동안에는 테스트가 실행되기 전에 수행해야 하는 일부 설정 작업이 있고, 테스트가 실행된 후에 수행해야 하는 일부 마무리 작업이 있을 수 있습니다.
Jest는 이러한 작업을 처리하는 헬퍼 함수를 제공한다.
2. beforeEach, afterEach
beforeEach는 모든 테스트 앞서서에 반복적으로 처리해야 하는 작업이 있다면 사용할 수 있다.
afterEach는 모든 테스트가 끝난 후 반복적으로 처리해야 하는 마무리 작업에 사용한다.
let num = 0;
//1
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num.toBe(1);
});
//2
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num.toBe(1);
});
//3
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num.toBe(1);
});테스트를 실행하면 같은 테스트임에도 2, 3번은 실패한다.
num의 값이 변경되기 때문이다.
우리가 2, 3번까지 테스트에 성공하기 위해서는 앞선 테스트의 결과가 뒤이어 실행될 테스트에 영향을 주어서는 안된다.
이때 beforeEach나 afterEach를 사용하면 된다.
let num;
beforeEach(()=>{
num = 0;
});
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num).toBe(1);
});
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num).toBe(1);
});
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num).toBe(1);
});beforeEach는 모든 테스트 앞서서 afterEach는 모든 테스트가 끝난 후 반복적으로 실행된다.
3. afterAll, beforeAll
그런데 만약에 우리가 DB에게 특정한 값을 받아서 num에게 대입한다고 가정해 보자.
let num;
beforeEach(()=>{
num = getData();
});
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num).toBe(1);
});
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num).toBe(1);
});
test('0 + 1 =', ()=> {
num+=1;
expect(num).toBe(1);
});테스트가 진행될 때마다 매번 계속해서 지속적으로 아주 많이 오랫동안 DB를 괴롭히게 된다.
또한 테스트 시간도 길어진다.
이런 경우 최초에 모든 테스트에 앞서서 단 한번 수행하거나 혹은 테스트 끝나고 단 한 번만 수행하고 싶다.
이때 beforeAll과 afterAll을 사용할 수 있다.
4. describe
let num;
beforeEach(() => {
num = 0;
});
test("0 + 1 =", () => {
num += 1;
expect(num).toBe(1);
});
test("0 + 1 =", () => {
num += 1;
expect(num).toBe(1);
});
describe("plus 2", () => {
test("0 + 2 =", () => {
num += 2;
expect(num).toBe(2);
});
test("0 + 2 =", () => {
num += 2;
expect(num).toBe(2);
});
});> jest ./test/beforeAfter.test.js
PASS test/beforeAfter.test.js
✓ 0 + 1 =
✓ 0 + 1 =
plus 2
✓ 0 + 2 =
✓ 0 + 2 =2를 더하는 테스트 코드끼리 묶어보았다.
describe를 이용하면 비슷한 테스트끼리 묶을 수 있다.
그런데 describe를 사용하면 실행순서에 변화가 생길 수 있다.
beforeAll(() => console.log('1 - beforeAll'));
afterAll(() => console.log('1 - afterAll'));
beforeEach(() => console.log('1 - beforeEach'));
afterEach(() => console.log('1 - afterEach'));
test('', () => console.log('1 - test'));
describe('Scoped / Nested block', () => {
beforeAll(() => console.log('2 - beforeAll'));
afterAll(() => console.log('2 - afterAll'));
beforeEach(() => console.log('2 - beforeEach'));
afterEach(() => console.log('2 - afterEach'));
test('', () => console.log('2 - test'));
});
// 1 - beforeAll
// 1 - beforeEach
// 1 - test // 1번 테스트
// 1 - afterEach
// 2 - beforeAll
// 1 - beforeEach
// 2 - beforeEach
// 2 - test // 2번 테스트
// 2 - afterEach
// 1 - afterEach
// 2 - afterAll
// 1 - afterAll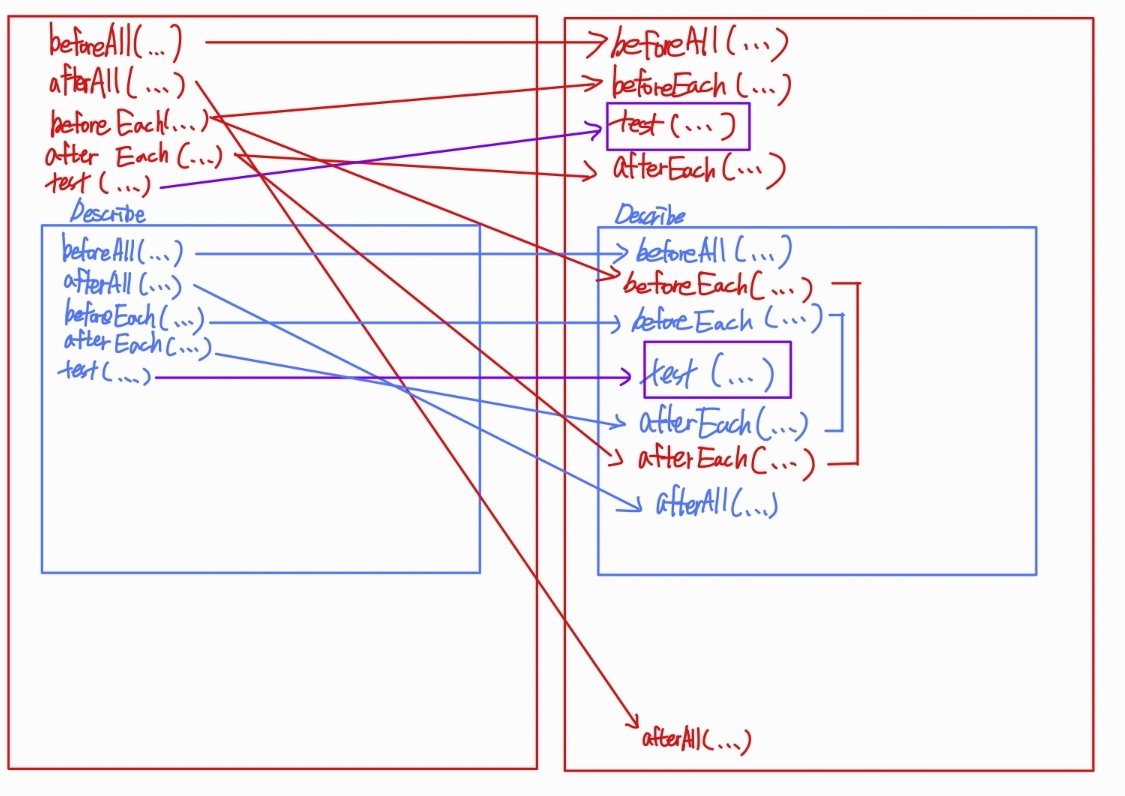
실행 순서가 복잡할 수 있으니 주의하자.
5. test.only & test.skip
test.only('this will be the only test that runs', () => {
expect(true).toBe(false);
});특정한 테스트만 실행하고 싶은 경우 test.only를 사용한다.
test.skip('this test will not run', () => {
expect('A').toBe('A');
});만약 특정한 테스트만 건너뛰고 싶은 경우 test.skip을 사용한다.
'공부 중 > Node.js' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Node.js] MySQL 제어하기 (0) | 2023.03.10 |
|---|---|
| [Nodejs] TypeError: Cannot convert undefined or null to object (0) | 2023.03.07 |
| [Jest] Testing Asynchronous Code (0) | 2023.03.01 |
| [Jest] Matcher (0) | 2023.03.01 |
| [Jest] node.js 테스트 프레임워크 (0) | 2023.03.01 |